Gaza unrest sends message about economic misery under Israeli blockade
Gaza (Reuters) – Weeks of violent protests by young men in Gaza have sent a message about the dire financial squeeze in the Israeli-blockaded enclave, economists and even some senior Israeli officials believe, and relief measures may be in the offing.
Ostensibly the protests, organised by youth groups but backed by Gaza’s ruling Islamist movement Hamas, were about the treatment of Palestinian prisoners in Israeli jails and visits by Jewish groups to the Al Aqsa mosque compound, a site holy to both Muslims and Jews, who know it as the Temple Mount.
But a senior Israeli official noted the relative restraint by Hamas, which did not officially join the protests itself or launch more rockets at Israel. He suggested the more immediate reason for the unrest was less long-time grievances related to the Palestinian national cause and more Gaza’s economic misery.
“The protests are about money,” said the Israeli official, speaking on condition of anonymity due to the topic’s sensitivity. “What we’re seeing on the (border) fence is a message. They are asking for financial help.”
Some 2.3 million people live in the narrow coastal strip, where per capita income is around a quarter the level in the Israeli-occupied West Bank and where over half the population lives below the poverty line, according to IMF estimates.
In the recent unrest, youths hurling stones and improvised explosive devices faced off against Israeli troops along the border fence who responded with live fire before calm was restored last week by Egyptian, U.N. and Qatari negotiators.
Sources close to the mediation said while some of Hamas’s demands are political, relaxing economic sanctions against Gaza is key to at least maintaining calm along the frontier.
The sources expect Israel, which along with Egypt maintains a tight blockade of the Gaza Strip that has helped cripple its economy, to announce further easings in coming days, including hundreds more permits for work in Israel.
Since 2021, when it fought a 10-day war with Hamas, Israel has softened some curbs on Gaza, offering thousands of work permits as well as measures to facilitate exports and improve its dilapidated utilities after years of underinvestment.
Fragile Ceasefire
A recent International Monetary Fund report said that for any stable long-term economic recovery in Gaza, “lifting of the blockade and easing of the Israeli-imposed restrictions are essential”.
It noted that Gaza had lagged far behind the West Bank over the past 15 years, mainly due to the years of isolation and repeated conflict after Hamas came to power in 2007, with 77% of households receiving aid, mainly cash or food.
With an official unemployment rate in Gaza of over 46%, Hamas itself has faced rumbling discontent over its economic management although for its part, the movement blames the Israeli blockade for the enclave’s economic woes.
“If there’s to be an explosion, let it be against the party that created these conditions, which is the (Israeli) occupation,” said senior Hamas official Bassem Naim.
Hamas leaders say any calm in Gaza will remain fragile unless Israel lifts the blockade and ends “aggressive measures and assaults in the West Bank and Jerusalem”, but they signal no interest in a new war.
Aware of the potential for worsening instability in Gaza, Israel has issued over 18,000 work permits to Palestinians there, which has allowed workers to bring in some $2 million a day and offered other forms of economic relief.
“The permit is everything for me, it is my life. If permits stop I will stop,” said Bilal Al-Najar, who took in 30-35 shekels ($7.70-$9.05) a day as a vegetable vendor in Gaza before earning 10 times more working in a restaurant in the southern Israeli city of Lod.
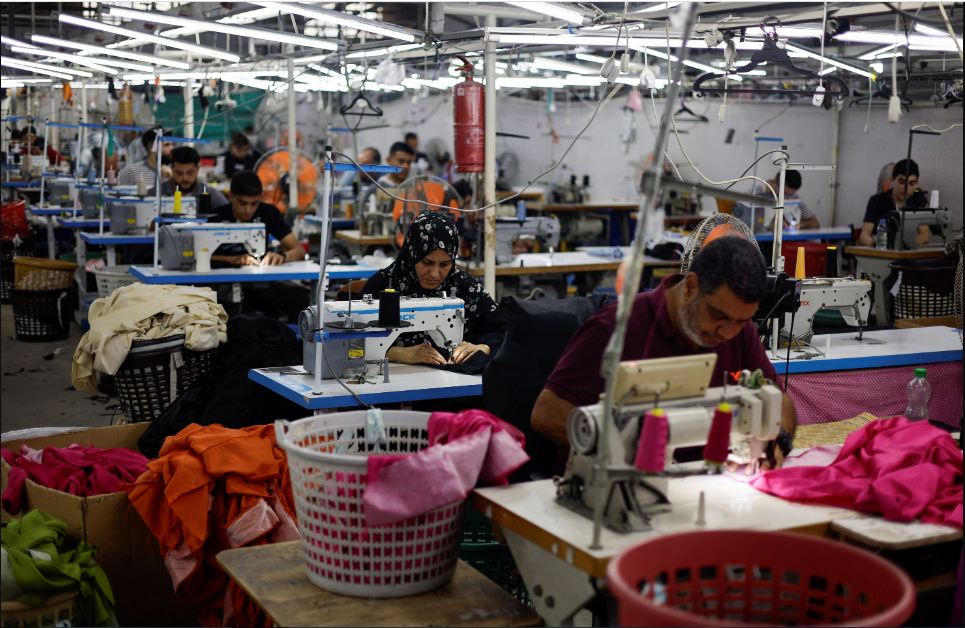
Gaza’s clothing sector, one of the main beneficiaries of any moderation of the blockade, has seen sales rise 10-fold since 2015, the year after an earlier war, and this year revenues look set to top the $22 million generated in 2022.
“If crossings are open, and the political situation is good this makes things in Gaza fit for a bigger revival both for work and for living,” said Bashir Al-Bawab, CEO of Unipal Company, one of Gaza’s largest clothing factories that have partnerships with Israeli companies.
But while Israel has offered economic incentives to avoid conflict, they are always liable to being cut off abruptly, exposing companies like Unipal, which exports 150,000 items a month to Israel, to constant uncertainty.
Last month, Israel imposed a brief blockade on exports from Gaza after inspectors said they uncovered an attempt to smuggle explosives into the West Bank. It then followed up by closing crossing points used by workers going to their jobs in Israel and the West Bank in response to the border protests.